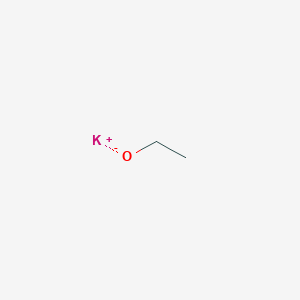
Potassium Ethylate Basic Information Potassium Ethoxide CAS No.917-58-8 potassium ethoxide,potassium ethoxide in ethanol,potassium methoxide solubility,potassium methoxide boiling point,potassium methoxide in methanol,potassium methoxide msds ShanDong YingLang Chemical Co.,LTD , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com
First, the seeds are strictly sterilized. Vigorously promote the purchase of selected and good quality coated seeds, eliminate seed carriers, and increase disease prevention and pest control. For cotton fields that do not use coated seeds, the cotton seeds used must also be treated with high-efficiency fungicides for seed dressing, boring, or soaking, and the seeds should be disinfected to prevent the seeds from spreading.
Second, timely sowing. The transgenic insect-resistant varieties have poor resistance to low temperature, slow emergence, weak seedlings, premature sowing, long emergence time, high nutrient consumption, multiple chances of seedling disease, and heavy onset. Therefore, sowing should not be too early or too late, and the principle of timely planting must be mastered. In the general cotton field, sowing is appropriate when the ground temperature of 4 cm is stable at 14°C; in alkaline cotton fields, sowing is appropriate when the ground temperature of 5 cm is stable at 15°C to 16°C.
Third, strengthen the field management of cotton seedlings. When the weather is dry, the cotton soil with poor soil moisture content should be timely sealed and put on seedling holes to protect the seedlings; when the soil moisture under the membrane is high, and when it is rainy, the time for closing the seedling hole can be postponed to the membrane. When the soil is loose and the soil temperature is suitable, the hole for seedlings should be sealed again to facilitate the spread of the disease and reduce the disease. In the open field, the soil should be insulated in time, the soil should be kept dry, the soil should be scattered, and the seedlings must be loosened; Timely setting seedlings, Qi Miao after the seedlings, grow 1 to 2 true leaves when a seedling, in order to facilitate the individual development of cotton seedlings and enhance disease resistance.
Fourth, chemical control, nutrition and strong seedlings. After the seedlings are set, the cotton seedlings are mixed and sprayed with fungicides and high-efficiency foliar fertilizers to prevent disease and strong seedlings. When the cotton seedling disease is first developed, it may be sprayed with "g-bacteria" or carbendazim or thiophanate-methyl, plus 0.2% potassium dihydrogen phosphate or more rare earth pure nutrients. At the peak of onset, it can spray 2,500 times evil spirit plus 3,500 times the amount of Tianfengsu, cotton seedlings diseased land, can be used alone 1000 times "bacterial absolutely" spray irrigation cotton seedlings. Cotton seedlings, usually 7-10 days to prevent and control once, continuous control 2-3 times, both to reduce hazards, reduce losses, but also to ensure the normal growth of cotton seedlings.
CAS: 917-58-8
MF: C2H5KO
MW: 84.16
EINECS: 213-029-0
Mol File: 917-58-8.mol
Potassium Ethylate Chemical Properties
Melting point 250°C (dec.)
Boiling point -78.5°C (rough estimate)
density 0.894 g/mL at 25 °C
refractive index n20/D 1.39
storage temp. Flammables area
solubility Soluble in ethanol, ether
form Powder
color white to off-white
Water Solubility It reacts vigorously with water.
Sensitive Moisture Sensitive
Stability: Stable, but highly flammable. Reacts violently with water. Contact with damp air may lead to heating of the solid, which could in turn ignite it, or materials with which it is in contact. Incompatible with air, water, moisture, acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, oxidizing agents, reducing agents.
Prevention and cure of cotton disease from the seedling stage
The disease at the seedling stage of cotton mainly includes blight, anthracnose, melasma, damping-off, and root rot. The main causes of cotton seedlings are seeds and soil carriers. Once they meet the climate and environmental conditions that are suitable for the disease, cotton seedling disease will occur seriously and damage the normal growth of cotton seedlings. The incidence of seedling disease in general is 30% to 50%. In recent years, with the promotion of transgenic insect-resistant cotton, cotton seedling disease has gradually increased, which directly threatens the early emergence of cotton seedlings and seedlings. Therefore, comprehensive prevention and treatment of diseases at the seedling stage of cotton has become a non-negligible safeguard measure for cotton production.