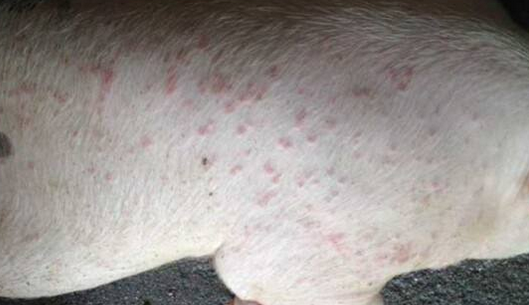
Porcine eczema is an allergic reaction caused by sensitizing substances in the epidermis and dermal epithelium. It is also called wet poisoning. It is characterized by more morbidity in summer and autumn rainy seasons and high temperature seasons. It is characterized by erythema, rash and itching in pig skin. It is divided into two types, acute and chronic. Loss of appetite after onset often leads to slow growth or stagnation, which causes great harm to pig production. First, the cause of the disease Poor sanitary conditions, damp heat fumigation, unclean skin, poor ventilation, and high stocking density. Single feed, lack of nutrition, especially vitamins, mineral deficiency and zinc deficiency. Insect bites, chemical irritations and chronic digestive tract diseases, metabolic disorders, endocrine disorders, etc. can also cause this disease. Second, clinical symptoms Most of the acute cases are sudden onset. At the beginning of the disease, the skin of the jaw, abdomen and perineum of the pig is red, and there are nodules such as soy bean size or broad bean size, itching, and blisters and papules appear when the condition is aggravated. Liquid, crusting and molting off. Acute pig treatment does not change to chronic in a timely manner. The skin of the sick pig is thick, infiltrating, itching, and often local infection, erosion or suppuration, which leads to the intake and rest of the affected, and finally loses weight and dies. Third, diagnosis Diagnosis can be made according to the season of onset. Sudden onset of acute, red skin at the beginning of the disease, itching, and later, papules and blisters appear wet after rupture. If there is a bruise, it is often accompanied by symptoms such as erosion, exudate, crusting and scaling. Chronic affected parts have less exudate, and the skin becomes thicker, itchy, and more scaly. Pay attention to the difference between skin diseases and other similar symptoms. Fourth, preventive measures The pig house is kept clean and dry, with good ventilation and light, and the grass is changed frequently. The humidity can be used to remove moisture from the lime, keep the skin of the pigs clean, and eliminate blood-sucking insects such as mosquitoes and flies. Strengthen feeding management, feed feeds rich in vitamins and minerals, diversify feed mix, digest feed easily, and reduce gastrointestinal irritation. In the treatment, decontamination and itching, washing, external hemorrhoids combined with injection or internal medicine. Five, treatment methods 1. Chinese medicine. Treatment of acute eczema: 40 grams of double flowers, 15 grams of Atractylodes, 15 grams of Forsythia, Sophora flavescens, Rhubarb, Poria, Yinchen, 30 grams of Yuanban, 15 grams of raw licorice, a total of research for the end, boiled water Or feed the feed. Treatment of chronic eczema: 20 grams of raw land and Sophora flavescens, 15 grams of angelica, white peony, medlar, medlar and white pelt, 30 grams of turf skin, 10 grams of licorice, a total of research for the end, boiled water or Mix the feed for feeding. 2. Western medicine. Acute eczema can be taken orally or intravenously with calcium chloride or calcium gluconate. Oral 5 to 10 grams of calcium gluconate daily, divided into two orally. Intravenous injection of 10% calcium gluconate 50~100 ml once daily. At the same time, oral administration or injection of vitamin A, vitamin C or multivitamin B. For the prevention and treatment of skin infections, sulfa drugs can be taken orally or by injection, and corticotropin can be used if necessary. 3. External use. Wash the skin once a day with 0.1% potassium permanganate solution. If there is more exudate in the affected area, apply 3%~5% gentian violet alcohol solution. Intermediate for CAS 175591-09-0 Tapentadol Hydrochloride Intermediate,Tapentadol Hcl,Tapentadol Hcl Api,Tapentadol Intermediates Shandong Bolode Bio-technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.bldpharma.com